© 2017-2019 Kunshan Feiya Precision Moulding Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. Site Map Designed by Alibaba
Injection molding is a semi-continuous process that involves injecting a melt of polymer or pressure ceramic (or rubber) into a closed and cold mold through a small hole called a grid. This molding material solidifies and begins to crystallize in semi-crystalline polymers. The plastic product is finally obtained by opening the mold cavity and removing the mold.
Injection molding is a popular technique for the manufacture of a wide variety of articles. In the United States alone, the plastics industry has grown at a rate of 12% per year for the past 25 years, and the main process is the transformation of plastic injection molding, followed by extrusion. An example of products manufactured by this technique range from the small play toys to the large automotive components.
Injection molding is a more environmentally friendly process compared to papermaking, forestry or chromium mining. It does not release gases or aqueous waste and has low noise levels.
The process has become popular due to the versatility of parts that can be manufactured, rapid manufacturing, scalable design of the rapid prototyping process, high production and low costs, high precision in the geometries, good dimensional tolerance and the ability to incorporate different colors.
Let’s look at the various components of the plastic mold and how the different components work.
The most important parts of the device are as follows:
Injection unit:
The main function of the injection unit is to melt, mix and inject the polymer. To achieve this, the pin of different characteristics are used as a polymer in the molten state. During the melting process of a polymer injection unit, three thermodynamic conditions need to be considered thus;
· The treatment temperature of the polymer.
· The heat of polymer capacity
· The latent heat of fusion, if the polymer is semi-crystalline.
The melting process
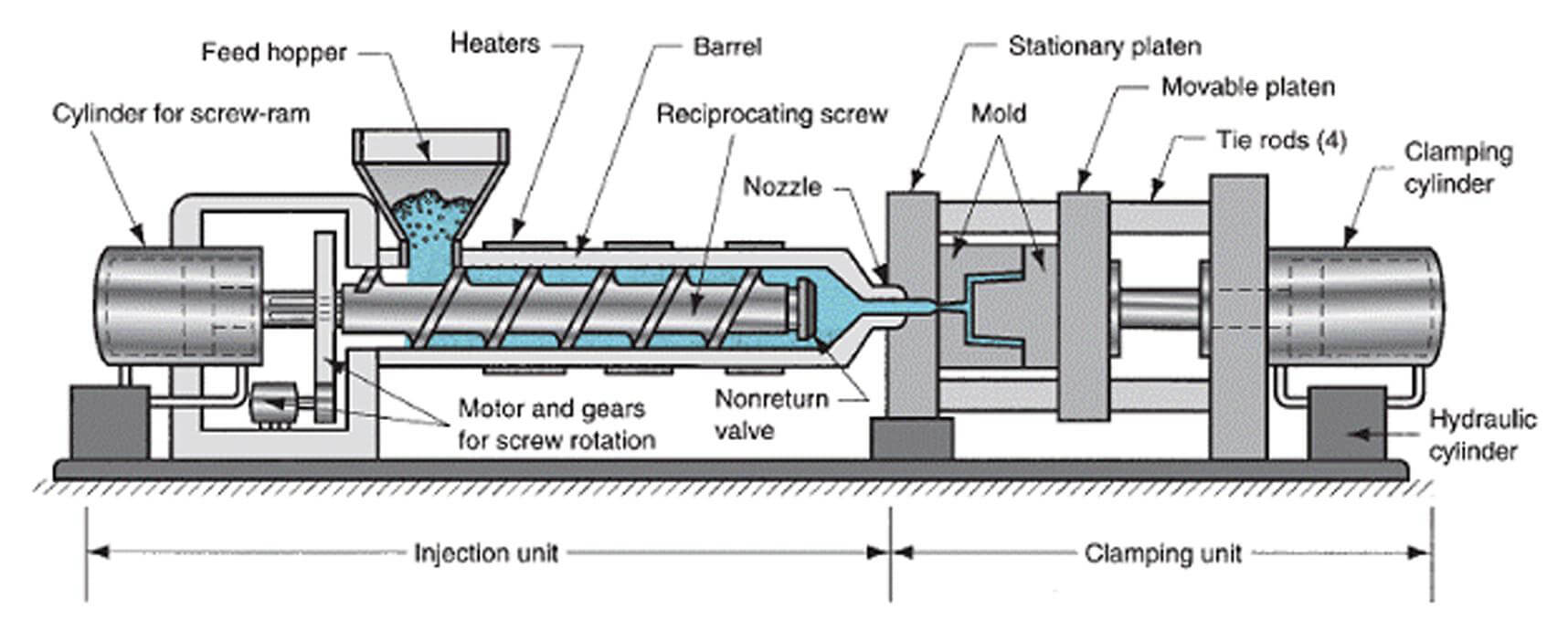
The melting process involves an increased heating of the polymer, resulting from an increase in temperature and friction between the cylinder and the screw. Friction and shear forces are essential for effective fusion because polymers are not good heat conductors. An increase in temperature and cutting speed also reduces the viscosity of the molten polymer. Thus, both parameters must be adjusted during the process. There are also standards for each polymer to prevent corrosion or metal degradation. With a few exceptions, such as PVC, most plastics can be used on the same process.
The injection unit is made up of a single screw extruder with a heating gun and sensors to maintain a constant set temperature. The depth between the channel and the spindle decreases gradually (or drastically, in special applications) from the feed zone to the dosing zone. Thus, the pressure in the cylinder gradually increases. The mechanical stress of cutting and compression system supplies heat to melt the polymer more efficiently.
An important difference in the injection process is the existence of an additional part called a reversing camera. This is where the molten polymer to be injected is accumulated. This chamber acts as a piston. All other units work when the piston pushes the material.